The ENVIROMUX Environment Monitoring Systems log data from their sensors, and send it to computers using Syslog.
Data Logging Using Syslog
| The ENVIROMUX Environment Monitoring Systems store event and data entries in the system data log. The system data log can be downloaded as a comma-separated plain text file (.csv), viewed via the web interface, or sent to up to 9 remote IP addresses using syslog. Data logging using Syslog on a remote computer allows for historical data collection in a convenient location. Linux/Unix-based computers use a standard syslog daemon to accept log data from the kernel, from any and all local processes, and even from processes on remote systems. Syslog support is not included on Windows-based computers, and will need a third-party application to accept the syslog alerts from the ENVIROMUX-MICRO or ENVIROMUX-1W. |
||
Configuring the ENVIROMUX-MICRO and ENVIROMUX-1W for Syslog |
||
| The ENVIROMUX-MICRO and ENVIROMUX-1W are easily configured to send log data to a syslog server based on the user selected. Access the User page by clicking "Administration", "Users", and then the "Edit" button next to the desired user. |
||
Example user syslog settings: (update image with attachment in email)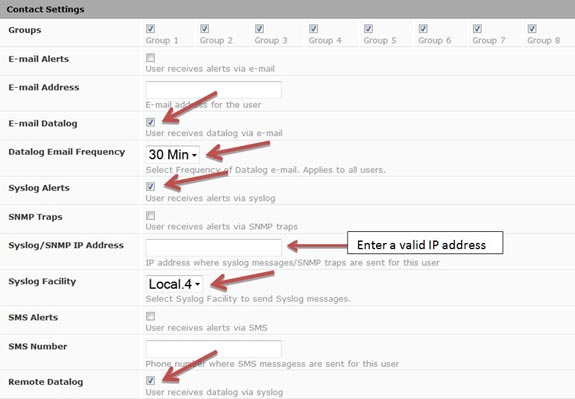 |
||
Checkmark or fill in the following sections as desired for Syslog data logging:
|
||
Configuring a Windows-based Syslog Server to Receive Syslog AlertsWindows-based computers do not include native syslog support, and will need a third-party application such as Kiwi Syslog (available as freeware with 30-day advanced options free trial) to receive syslog alerts. The software can be installed either as a stand-alone application, or installed as a service running uninterrupted in the background. Installing the software as a service doesn't require the user to login to Windows to accept syslog messages. Example Operating Mode: 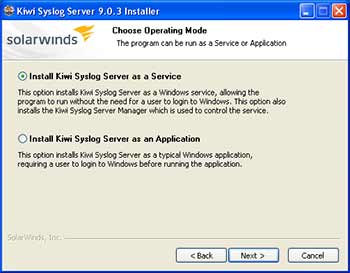
Once installed, the software can be setup to filter syslog alerts by priority and facility. In the Service Manager window, click the "File" menu, and then "Setup" to access the settings for the software. Right click the "Filters" submenu underneath "Default" in the "Rules" section of the menu, and click "Add filter". Rename the new filter accordingly, and hit enter to apply the name. Click the new filter's name to access the settings for that filter. Select "Priority" from the "Field" drop down list above to bring up the options for filtering incoming syslog messages. The chart shown categorizes each facility to the left, and priorities on the top. Example Priority and Facility Filter: 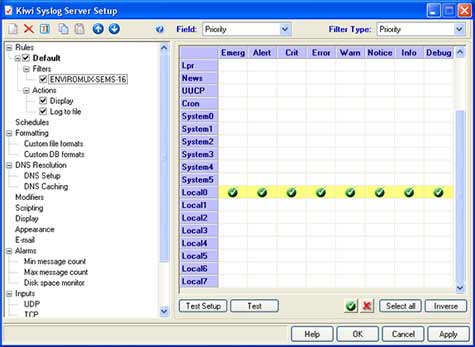
Click "Apply" to accept the settings, and "OK" to exit the Setup window. The default settings on the other options in the Setup window can be modified to fit individual needs of the user, but of particular importance is the "UDP" menu item under "Alarms". These default settings are standard remote message settings for syslog, and should not be changed. Example UDP Settings: 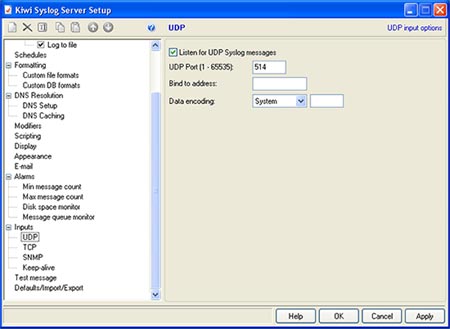
The software should now be ready to accept incoming syslog messages from the ENVIROMUX-MICRO. |
||
Configuring the Linux/Unix-based Syslog Server to Receive Syslog AlertsThe standard syslog daemon used by Linux/Unix-based systems is configurable to accept alerts from remote systems. To configure the system to receive these alerts, two configuration files will need to be edited: /etc/sysconfig/syslog (/etc/init.d/sysklogd on some systems) and /etc/syslog.conf (/etc/rsyslog.conf on some systems). Example syslogd configuration:
Save the changes to the syslogd configuration, and restart syslog to apply the changes. Example restart syslog command:
The system firewall may also need to have port 514 opened as well. |
||
Filtering Received Syslog AlertsAt this point, the received syslog messages are being written to the same file as many other system messages and alerts. Syslog writes each type of message received based on the settings in the /etc/syslog.conf (/etc/rsyslog.conf on some systems) configuration file. The syslog configuration file can be modified to isolate the messages coming from the ENVIROMUX-MICRO or ENVIROMUX-1W for easier access. The file consists of two columns, first listing the facilities and severities of messages, and the second listing the files to which they should be logged. By listing the full path to a filename as a line's action in syslog.conf, messages that match that line will be appended to that file. Example syslog.conf file configuration
Restart syslog again to apply the changes. |
